Quickstart
Requirements
Step 1 — Install Garden
brew install garden-io/garden/garden-clicurl -sL https://get.garden.io/install.sh | bashSet-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force; iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/garden-io/garden/master/support/install.ps1'))Add-MpPreference -ExclusionPath "C:\Path\To\Your\Repo\.garden"Step 2 — Clone the example project
git clone https://github.com/garden-io/quickstart-example.git
cd quickstart-exampleStep 3 — Connect your project
Step 4a — Deploy the project to local Kubernetes
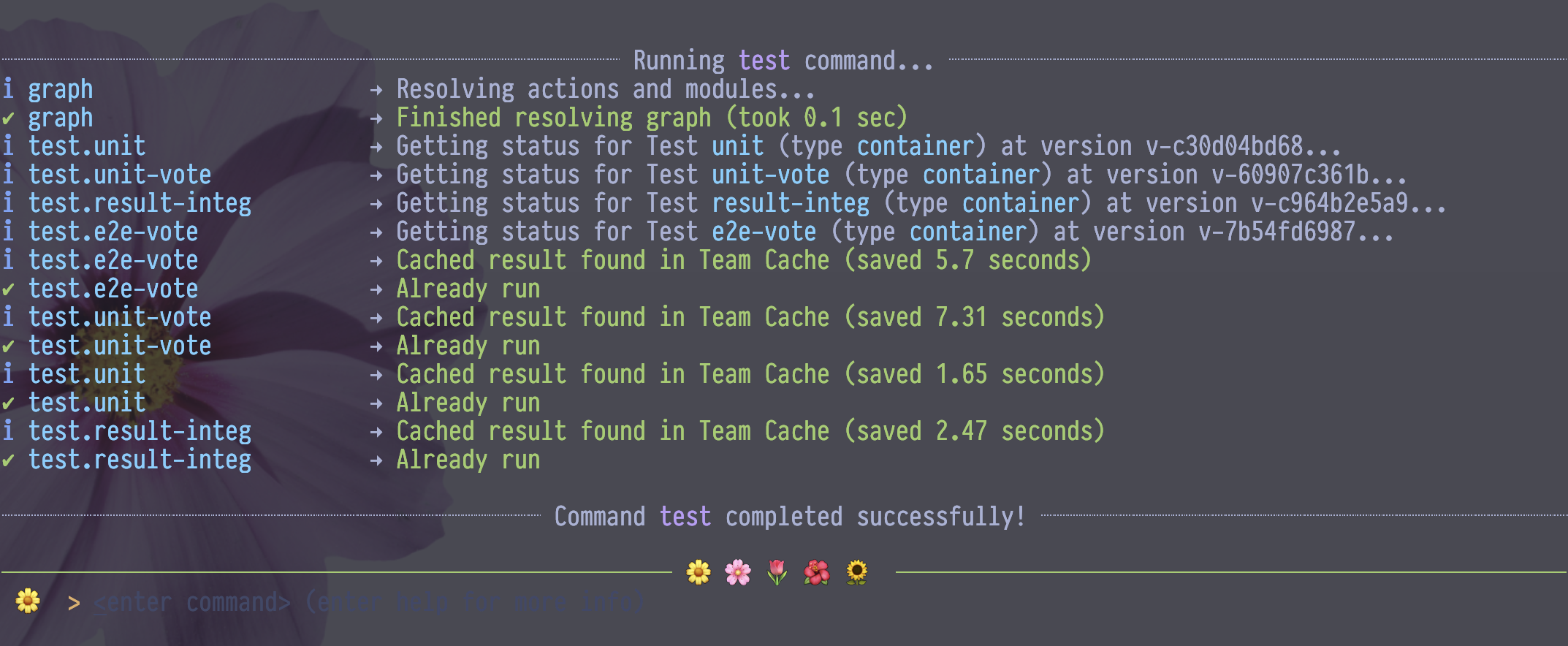
Step 4b — Build the project without Kubernetes
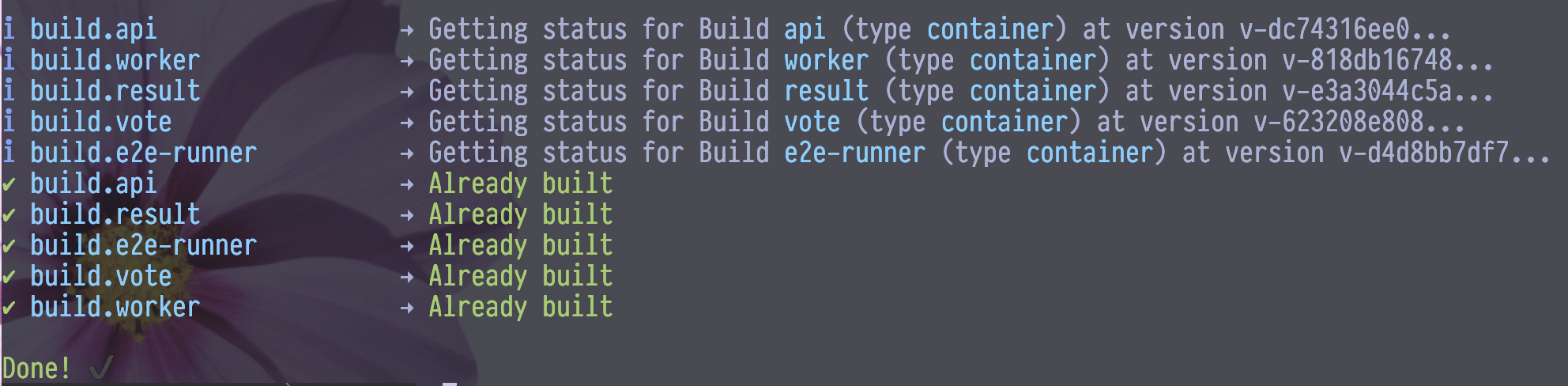
Next Steps
Troubleshooting
PreviousSlite - "Garden is the best companion for a Kubernetes dev, from local envs to CD."NextGarden Basics
Last updated
Was this helpful?

